Introduction to Edema and Its Common Causes
Edema, commonly referred to as water retention or swelling, is a condition characterised by an accumulation of fluid in the tissues, causing parts of the body such as feet, hands, and joints to swell. In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), edema is often seen as a result of a disharmony within the body’s Qi (energy) and a dysfunction in the kidney, spleen, and lung systems that manage fluids.
How Acupuncture Addresses Edema
Acupuncture, a core component of TCM, offers a natural remedy for swelling by promoting the body’s self-healing mechanisms. It involves the insertion of fine needles into specific points on the body to balance Qi. According to TCM theory, the proper flow of Qi is essential for health, and disruptions in this flow can lead to issues like fluid retention.
TCM Diagnosis of Edema Causes
In TCM, the diagnosis of edema involves understanding the underlying imbalances causing Qi stagnation and fluid accumulation. Commonly, edema is attributed to a weakness in the spleen’s ability to transport and transform fluids, which can lead to an accumulation of dampness. The kidney is also often involved, as it plays a critical role in water metabolism and can contribute to swelling if its Qi is weak.
Acupuncture Treatment Strategy
Acupuncture treatments for edema focus on stimulating points that strengthen the spleen and kidney, enhance the body’s diuretic functions, and promote the elimination of excess fluid. For instance, points such as Spleen 6 (SP6) and Kidney 3 (KD3) are targeted to invigorate these organs’ functions. Additionally, Lung 7 (LU7) might be used to assist the lung in dispersing fluids and aiding the upper body in managing water retention.
For those interested in exploring how personalised acupuncture treatments can help manage conditions like edema, our clinic offers a specialised approach. Learn more about our edema and water retention acupuncture treatments at Yi Acupuncture to see how we can tailor therapy to meet your needs.
Herbal Medicine Complements Acupuncture
Alongside acupuncture, herbal treatments are also utilised to treat edema. Herbs like Poria (Fu Ling) and Cinnamon Twig (Gui Zhi) are used in concoctions to enhance the body’s natural fluid metabolism and support the spleen and kidney health.
Other herbs also used in common formulas for the treatment of edema include: Licorice (Gan Cao), White Atractylodes (Bai Zhu).
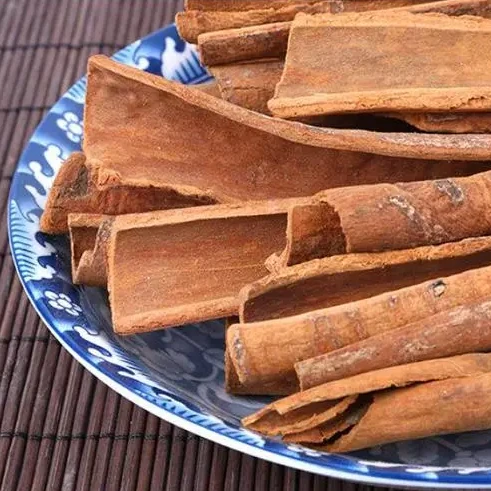
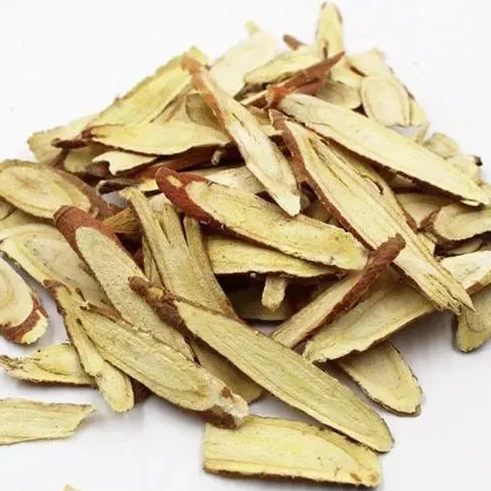




Herbal Formula
There is a standard herbal formula called Ling Gui Zhu Gan Tang, which is used to promote water metabolism, and balance water distribution.
- Fu Ling: 12g
- Gui Zhi: 9g
- Bai Zhu: 6g
- Gan Cao: 6g
A good TCM practitioner will usually customise the formula, according to the patient’s needs.
Lifestyle and Dietary Recommendations
Managing diet and lifestyle is crucial in supporting the treatment of edema. TCM advises reducing the intake of salt and processed foods, which can exacerbate water retention. Foods rich in natural diuretics such as cucumber, celery, and asparagus are recommended. Regular physical activity is also encouraged to improve circulation and fluid balance.
Diabetes and Its Link to Edema
Diabetes is commonly associated with various complications, one of which is edema, particularly in the lower legs, feet, and ankles. Edema in diabetic patients can result from a combination of factors including poor circulation, heart problems, and kidney damage. The condition of persistent high blood sugar levels can lead to damage in the capillaries (small blood vessels), which results in the leakage of fluid into surrounding tissues, causing swelling.
In the realm of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), diabetes-related edema is treated by addressing not only the swelling but also the underlying imbalances that contribute to the diabetic condition. Acupuncture points may be specifically chosen to enhance kidney and spleen function, which can help manage blood sugar levels and improve circulation, thus reducing the risk of edema. Moreover, specific herbal formulas aimed at strengthening these organs and promoting fluid balance are often recommended, providing a holistic approach to managing both diabetes and its symptoms like edema.
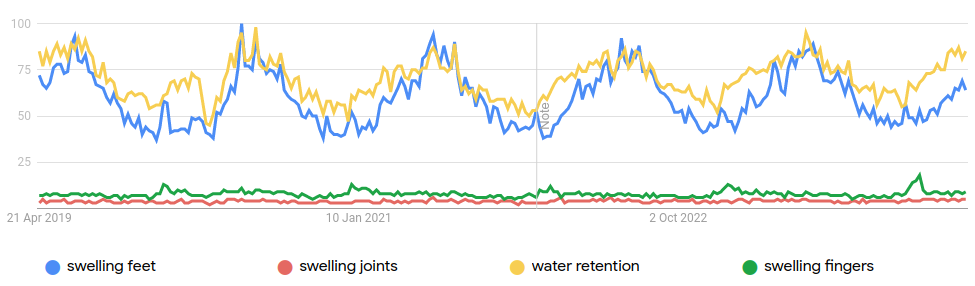
Seasonal Variations in Swelling and Water Retention
The incidence of swollen feet and water retention often exhibits noticeable seasonal patterns, peaking typically during the warmer months. Higher temperatures lead to the expansion of blood vessels, which can exacerbate fluid retention, particularly in the lower extremities. Additionally, people tend to be more active during summer, which can further contribute to swelling. Understanding these seasonal trends can help individuals preemptively manage symptoms through timely acupuncture treatments and adjustments in diet and lifestyle. Engaging in regular cooling exercises, increasing the intake of natural diuretics, and staying hydrated are effective strategies for reducing the impact of heat-induced edema.
Conclusion
Acupuncture and herbal medicine provide effective natural remedies for managing symptoms of edema, swelling feet, and water retention. By addressing the root causes of fluid imbalance through the lens of TCM, individuals can find significant relief and improvement in their overall well-being.